Table of Contents
What is an Internet Exchange Point
An Internet Exchange Point (IXP) is an open neutral interconnect where network operators can freely interconnect for the purpose of exchanging traffic.
Definitions
Open means that the physical infrastructure provided for interconnecting networks is open to any and all network operator to participate in, as they wish. Each network operator is responsible for providing their own connectivity to the public interconnect location.
Neutral means that the physical infrastructure provided for interconnecting networks is not owned or operated by any network operator who'd participate in the IXP. It is important that each member of the IXP has equal opportunity to participate and there is no perception of advantage for any one member.
Freely means that the network operator participating in the Internet Exchange Point can choose who they peer with according to their own business requirements.
IXPs are typically hosted in or by data centre or data housing organisations or other entities such as Universities who operate 24x7 data centre facilities.
Participation
(UPDATED)
Any network operator can participate in an Internet Exchange Point. The only requirements are:
- they have their own public IP address space
- they have their own public AS number
- they have their own transit arrangements
- they are able to configure and use BGP (the Border Gateway Protocol)
IXP participation is not limited to just commercial Internet Service Providers. Research & Education network operators, enterprises (small to multi-national), content providers, gTLD and ccTLD DNS operators, content distribution networks, Universities, broadcasters & media, etc all participate at IXPs. The only requirements are the Internet resources mentioned above.
Note: Connecting to an IXP means only getting access to the other operators participating at the IXP. Connecting to an IXP does not mean getting a connection to the whole Internet - hence the requirement for IXP membership clearly stating that members must have their own transit arrangements.
Location
IXPs are located where it is most convenient for the largest number of network operators to access and participate at the most optimum cost to the network operators. (Bearing in mind that peering is designed to minimise the cost of operation for network operators.)
Ideal locations for public interconnects include datacentres and/or locations of concentrations of fibre provided by several infrastructure operators. These locations all have:
- Good physical access (for members to carry out maintenance as required)
- Good network access (choice of infrastructure suppliers)
- 24 hour on-site operator coverage (“hands” on-site in case of urgent issues)
- Independent power supplies with on-site backup (seamless battery backup with generators; diverse power feed from the grid)
- Sufficient cooling (air-conditioning, as required)
- Good protection from natural disasters (earthquake, tsunami, wildfire, floods, volcanoes, cyclones).
- Good physical security (so that only the clients of the location have fully managed and verified access)
Given the large concentration of network operators present, these public interconnects are often considered critical infrastructure, and their reliable operation is often considered of national importance.
Physical Infrastructure
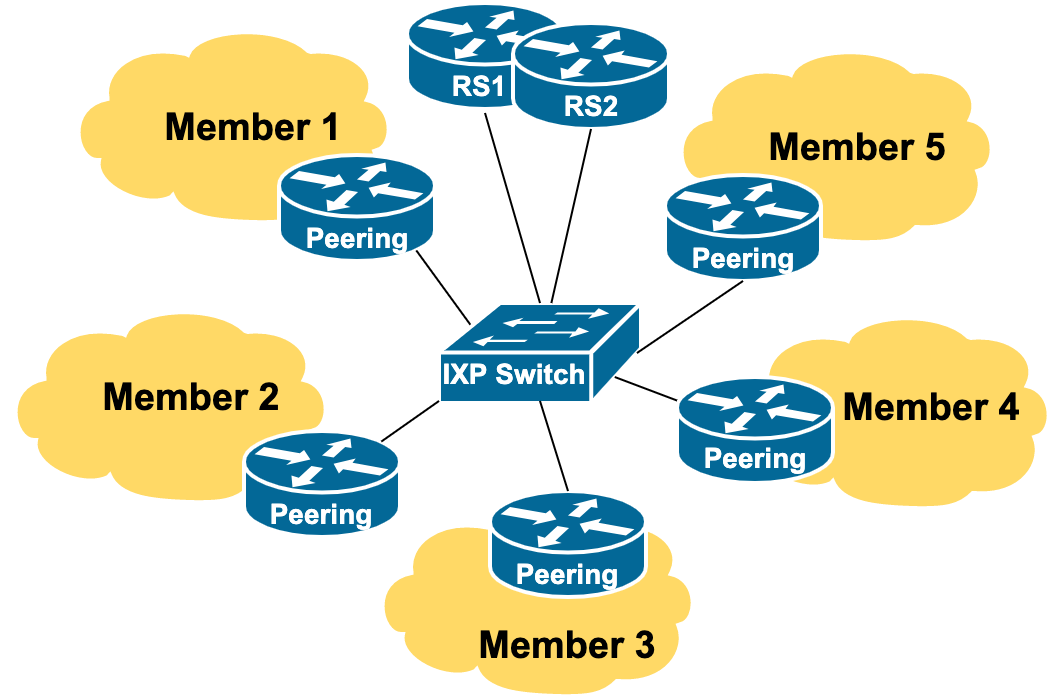
The interconnect medium of the IXP itself is just an ethernet switch.
The basic ethernet switch used for most new IXPs today tends to be a 24 port or 48 port fibre switch supporting dual personality 1G or 10G ports. The port's behaviour is determined by the Small Form-factor Pluggable Transceiver (SFP) installed in the port.
The simplest IXPs have little more than an ethernet switch to support interconnections by the participants. As a concept, they'd look like this (details discussed elsewhere in the Toolbox):
The world's largest IXPs operate multiple switches over multiple locations in the metro area, and provide services and facilities for the benefit of all the members.
Administrative Structures
There are a few different ways that IXPs are set up and operated - the most common are:
Member Organisation
This is the simplest form of IXP where each member contributes a small fee towards the annual operating cost of the IXP. Each member has a stake in the IXP, each member has a say in how the IXP operates.
Given most members of an IXP are highly competitive commercial entities, there needs to be a structure that ensures that no member is seen to get competitive advantage over the other.
To support the IXP, there is usually a non-profit organisation or member association created (depending on local laws and regulations). Each member is represented on the management board (for the smaller IXPs) or representatives from the members (for the larger IXPs).
There are several ways these IXPs operate, depending on the funding models chosen. Some have sufficient funds to hire full time staff to operate the switch fabric and services supporting the exchange. Others outsource the operation to a third party on contract. Others simply have each member volunteering to take turns at running the basic fabric.
Datacentre Hosted
This form of IXP is common for many data centre operators around the world. The IXP is provided for the customers of the data centre, and all customers can potentially benefit from interconnecting their networks for settlement free peering.
The IXP in this case is operated entirely by the data centre for the participants. The participants have no say in how the IXP operates. However the data centre is very focused on customer requirements which ensures the IXP operates for customer benefit.
Fees to connect depend entirely on how the data centre operator wishes to operate the facility - quite often there is no fee as the presence of the IXP is value for the data centre operator itself. Sometimes there are port charges as the various ethernet switches used tend to be more pricey the bigger the interfaces needed by the members.
Commercial
Very similar to the datacentre hosted IXP but, rather than being operated by the data centre, they are operated by a commercial entity on behalf of the members.
The IXP in this case is operated entirely by the commercial operator for its customers. The participants/customers have no say in how the IXP operates. However the commercial operator is very focused on customer requirements (and potential competition) which ensures the IXP operates for customer benefit.
Fees to connect depend entirely on how the commercial operator wishes to operate the facility. Usually there are port charges as the various ethernet switches used tend to be more pricey the bigger the interfaces needed by the members.
Agreements
Operators who participate at an IXP usually will sign an agreement with the IXP itself. This agreement usually contains information such as:
- contact details of the Peering Coordinator (the administrative contact) at the operator
- contact details of the Network Operations Centre at the operator (not customer helpdesk!) and the IXP
- escalation process in case of faults on the interconnect
- rules/behaviour at the IXP
- how to use IXP infrastructure to aid with setting up connections with other operators
- any other relevant information relating to the connection at the IXP to ensure its continuous and reliable operation
Not all IXPs require such an agreement although it is recommended simply so there is a documentation trail and that the operator knows what to do if any issues need to be resolved.