This is an old revision of the document!
Transit
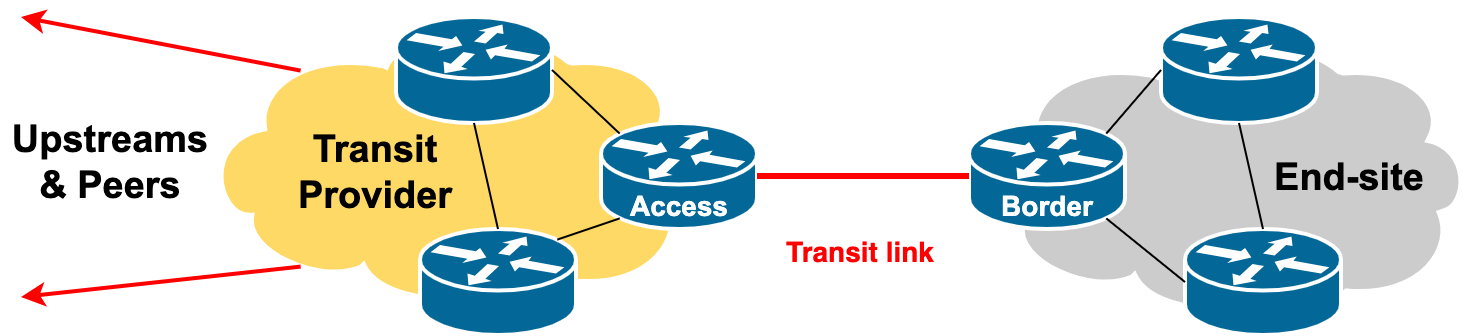
Transit is the purchasing of Internet access by a network operator from another network operator (known as their upstream provider).
The vast majority of transit attracts traffic charges. Charges are normally levied on traffic levels (typically measured in US$ per Mbps per month). Charges vary from region to region, and the quantity committed to. For example, committing to 100Mbps will attract a much higher charge per Mbps than committing to 1Gbps would.
Some locations charge based on outright volume (usually of downloads, but some combine both downloads and uploads), which can make Internet access very expensive. This method is reminiscent of legacy telephony plans which permit so many calls per month, or mobile data plans allowing the user so many call minutes and/or Gbytes of download per month.
The choice of a transit provider is beyond the scope of the Peering Toolbox; however typical considerations include (in no particular order):
- cost
- reliability
- service quality
- latency
- bandwidth
- the transit provider's diversity of peering and transit arrangements
TO BE DONE
Public peering takes place at a public peering point, commonly known as an Internet Exchange Point (IXP).
Public peering is how network operators scale private peering - a large number of private interconnects with different network operators starts becoming expensive and more challenging to manage. So rather than having many private interconnects with other operators, it is more cost effective, and operationally straightforward, to connect to a public interconnect where all operators meet, and peer with all of them there.
This may seem counter-intuitive when commercial network operators all compete with each other, but each competitor knows that they improve their cost and quality of operation by interconnecting with their competitors.
As a newcomer network operator is scaling their operations, it becomes high priority for them to participate in their local Internet Exchange Point.